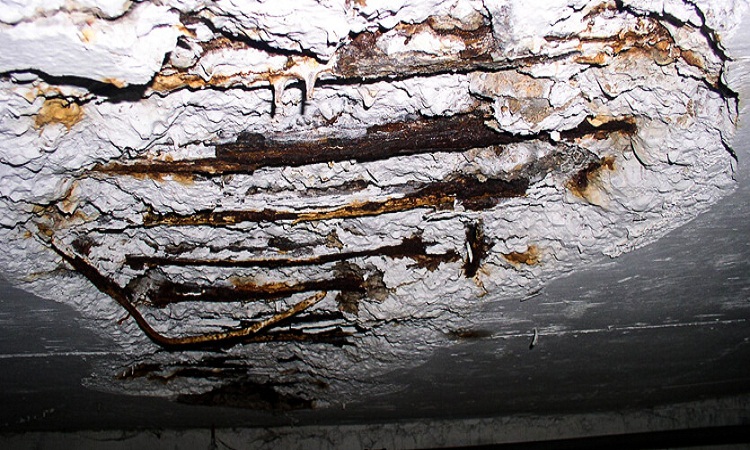
Concrete repair is the procedure of fixing a hardened concrete surface that over time has lost the ability to hold the binding concrete materials together because of environmental exposure or damage. Concrete repair is appropriate for cracks, physical impacts, surface scaling, or chipped-out surfaces. Why Does Concrete Needs Repairs? There…
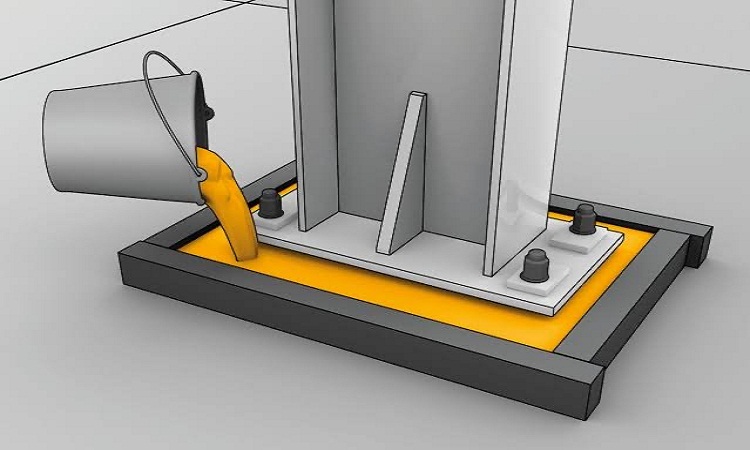
What is Engineering Grout? Its Types, Properties, Applications
Engineering grout is a material that has properties on non-shrink, free flow, high early strength for bolt pocket, and base plate of machines to ensure firm and vibration-free equipment. Engineering grout is composite material generally consisting of water, cement, and sand. Engineering grout is normally utilized for filling voids under…
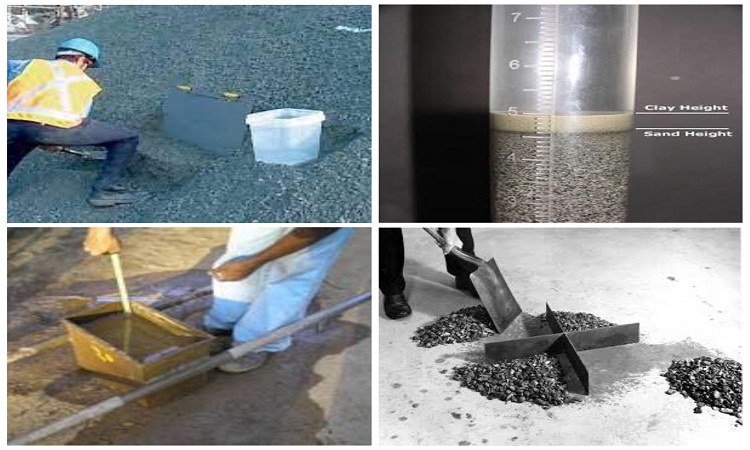
Different Field Tests of Aggregates
There are simple field tests of aggregates that are required to be carried out in the field to enable the site supervisor to determine the quality and the proportions required to be taken in the concrete mixes. Before the tests are performed, it is very important to collect a proper…
What are the Properties of Aggregates for Concrete?
In concrete, fine aggregates and coarse aggregates make up about 75% of the total concrete materials. It is, therefore, significantly important to acquire the right type and quality of aggregates at the site. The aggregates from the main matrix of the concrete/mortar. The aggregate particles are glued together by the…
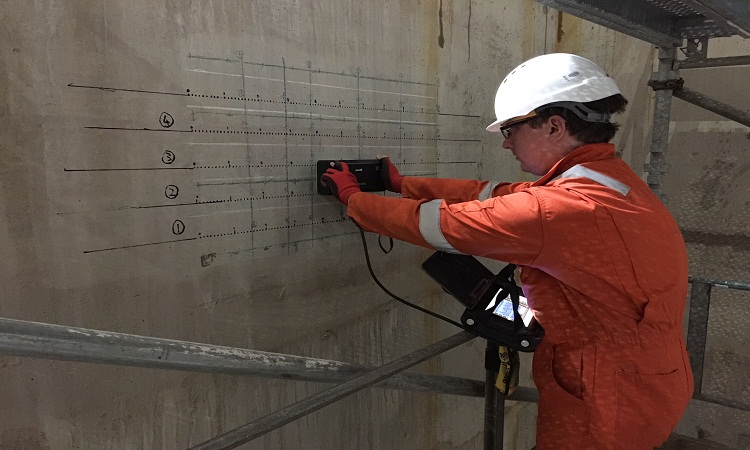
What is Structural Appraisal? Principles and Guidelines for Structural Appraisal
A structural appraisal is concerned with establishing the strength of an existing structure and reporting on its safety & its fitness for a given purpose. As the structure being appraised exists, many uncertainties that existed and assumptions made during its original design can now be incorporated into the appraisal review…
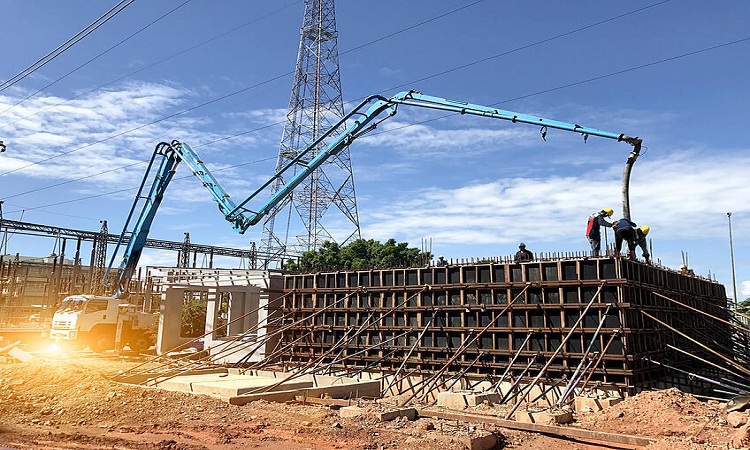
Checklist for Pumped Concrete, Site Planning, and Precautions
Pumped concrete moves as a cylinder riding on a thin lubricating film of grout/mortar on the internal diameter of the pipeline. Before pumping begins, the entire pipeline’s interior diameter must be coated with either grout or a specialized commercial primer using the methods for 100% coating of the pipe walls…
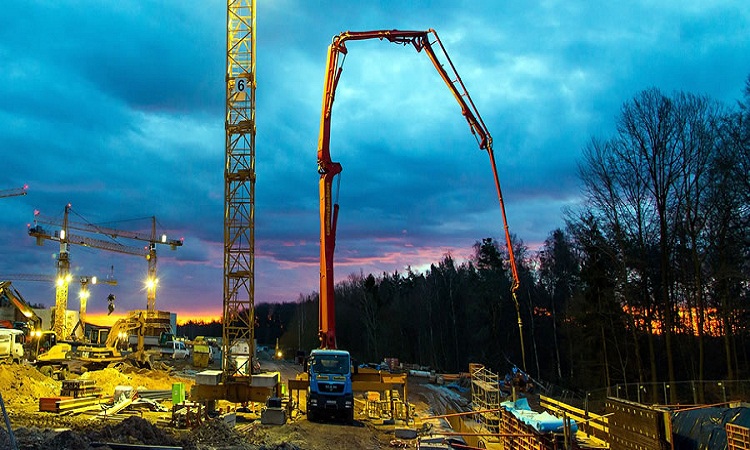
What is Pumped Concrete? Advantages and Disadvantages of Pumped Concrete
Pumped concrete is the concrete that is transported to heights by means of pumping using concrete pumps. Pumped concrete is utilized where a large quantity of concrete work is involved at a greater height, where different methods of transport are not easy to do. Concrete pumps have been known for…
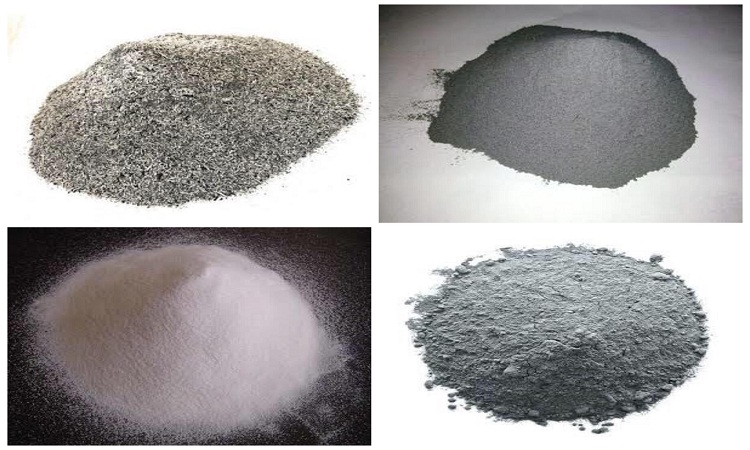
Mineral Admixtures – Its Types, Advantages and Their Effects on Concrete
Mineral admixtures are mostly derived from other substances and not chemically manufactured. Mineral admixtures make concrete mixtures more cohesive, economical, reduce permeability, increase strength, and influence other properties of concrete. Mineral admixture impacts the nature of the hardened concrete through hydraulic activity or pozzolanic activity. Pozzolanas are cementitious materials and…
What is Durability of Concrete? Factor Affecting Durability of Concrete
The durability of concrete is defined by its capability or the ability to resist weathering action, chemical attack, abrasion, or any other deterioration process and retain its original form, quality & serviceability when exposed to its environment. Different concretes require different degrees of durability on the exposure environment and properties…
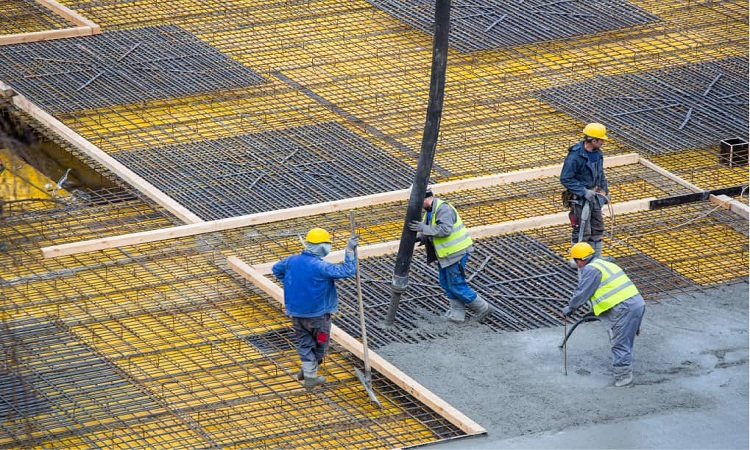
Placement of Concrete – Recommendations for Concrete Placement
The concrete placing method will depend on the rate of concreting planned, type of structure, the quantity of concrete required to be poured in one go, the equipment or manpower available for placing and compacting concrete, formwork design, the time required for the initial setting of concrete, and even the…