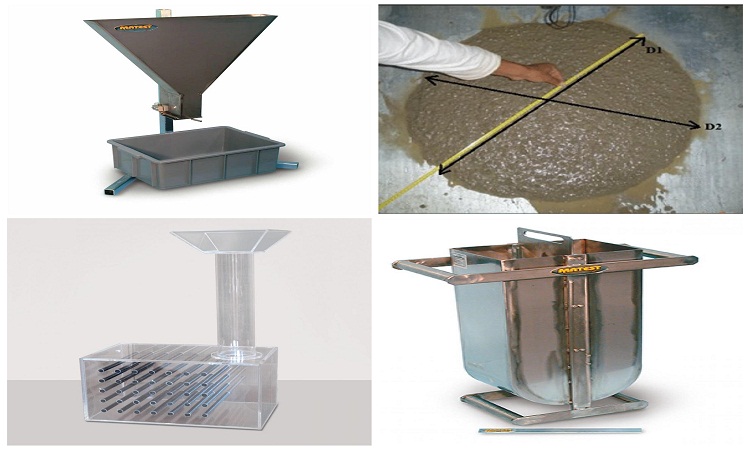
There are three basic properties of self-compacting concrete (SCC) namely flowability, passing ability (free from blocking due to presence of reinforcement), and resistance to segregation (stability/homogeneity). Therefore, it is very essential to carry out field trials or mock trials to assess these attributes. Unfortunately, so far not a single test has been devised to confidently measure any one of these characteristics of concrete. Several tests have been found out and utilized by many organizations but all these tests are elementary in nature and none of the tests has been standardized.
The most commonly used tests for self-compacting concrete are the Slump Flow Test, “V” Funnel Test, “L” Box Test, ‘U’ Box Test, and Fill Box Test. In addition to these all tests there are other tests like the ‘J’ ring test, etc. The first five tests are briefly described below:
Slump Flow Test
This is one of the easiest and simplest tests initially developed in Japan for the analysis of underwater concrete. The slump flow test is the most commonly used test for self-compacting concrete (SCC) and gives a good assessment of filling ability. Though, it gives no indication of the ability of the concrete mix to pass between the reinforcement without blocking but may give some signals on resistance to segregation of materials. This test can be utilized at the site location to analyze the consistency of supply of ready mix concrete, which has been designed after assessment of various characteristics based on the above mentioned five tests or more.
The procedure & execution of the Slump Flow Test is briefly explained below. The test procedure for the execution of the slump flow test is as follows:
- Position the slump cone at the center of the leveled flow table.
- Pour the concrete with a scoop from the top without any tamping to fill the slump cone completely. Strike off excess concrete.
- Lift the cone vertically without any jerks & allow the concrete to flow freely on a leveled surface.
- Note the time required for the concrete to flow 50 centimeters (cm) diameter spread circle. The time is measured from the time the lifting cone starts.
- After concrete stops flowing, measure the average flow diameter of concrete.
- This value in millimeter (mm) is known as slump flow value in mm.
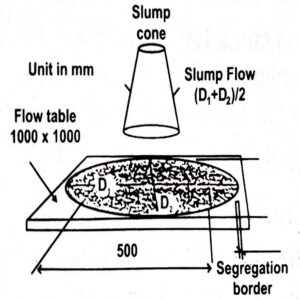
Slump flow is the average diameter in 2 perpendicular directions of the concrete spread after the concrete had stopped flowing on leveled flow table. The slump flow time is the time taken for the concrete to spread by 50 cm. A high slump flow value specifies greater flowability & lower resistance to segregation of materials. If the time value is perceived to be less than the minimum range value identified then it indicates that viscosity is very low leading to segregation. If the time value is observed to be more than the maximum range value specified, it indicates very stiff and non-flowable concrete.
The acceptable range of value for slump flow is 650 mm – 800 mm.
V Funnel Test
V Funnel Test is designed to analyze the flowability & also segregation resistance of self-compacting concrete.
The procedure for the implementation of the test is as follows:
- Position the ‘V’ funnel apparatus along with supporting arrangement on level ground.
- Moisten the inner surface thoroughly with a wet sponge and close the trap door.
- Pouring the concrete mix from the top of the funnel without any external efforts either to compact or level it.
- Open the trap door very quickly as far as possible after filling the funnel without giving any shake to the test setup.
- Note the time necessary to clear the funnel completely in seconds, which is T0.
- Repeat the same procedure with only change that the trap door is opened after 5 minutes of filling totally and note the time needed to empty the funnel totally in seconds, which is T5.
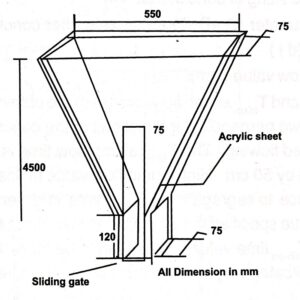
As per the current guidelines, T0 from the test should be in the scale of 8 to 12 seconds and T5 should be less than 3 seconds over T0. If T5 is greater than 3 secs over T0 then there are some chances that the Self Compacting Concrete (SCC) mix will segregate.
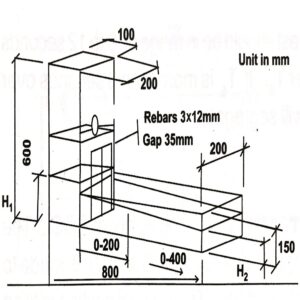
L Box Test
L Box test is utilized mainly to analyze the passing & filling ability of self-compacting concrete (SCC). The instruments for the L box consist of an “L” shaped rectangular box section. The concrete mix is designed to pass along the obstructions of known clearances. The vertical section of the box is filled with concrete & the gate is uplift to let the concrete flow into the horizontal section along the vertically placed steel bars. When the flow of concrete stops the height of the concrete mix (h2) at the end of the flow is measured along with height (h1) in the vertical box next to the obstruction. The ratio h2/h1 is a measure of the passing ability of self-compacting concrete (SCC). The blocking value for self-compacting concrete (SCC) should be between 0.80 to 1.0. If the blocking value is lower than 0.80 it suggested that viscosity is too high. A ratio close to 1, indicates false results.
Both segregation resistance & passing ability can be identified during the test visually also. If concrete forms a plateau in front of reinforcement steel bars, concrete has either got blocked or has segregated.
The procedure for performing this test is briefly discussed below:
- Place the ‘L’ box on firm/level ground.
- Moisten the internal surface thoroughly & close the trap door.
- Completely fill the vertical section of the L Box with a concrete mix.
- After a minute lift the gate of the apparatus without any jerk.
- Take the measurement of the height of the concrete mix at the obstruction (h1) and at the end of the flow (h2).
- With respect to the base/bottom of the L box.
- The ratio of h2/h1 as measured above provides the blocking value of Self Compacting Concrete.
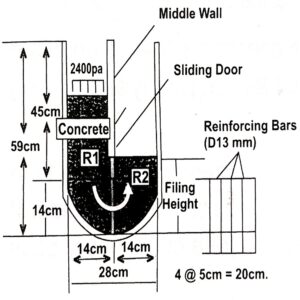
U Box Test
This test is used to assess the passability of self-compacting concrete (SCC).
This apparatus has a “U” shape and an opening with a sliding gate is fixed between the two sections with vertical steel bars as obstructions. Concrete is designed to flow through the obstructions & the level difference between the top surfaces of concrete in both the compartments is measured.
The method for performing U Box test is briefly discussed below:
- Place the ‘U’ box on firm/level ground.
- Moisten the inner surface thoroughly & close the central door.
- Fill the concrete mix in the left compartment totally.
- Wait for some time and lift the gate without any jerk & let the concrete flow on leveled ground.
- Clean the slurry adhered to the face of the left compartment without disturbing the top surface of the concrete to increase visibility.
- Take the measurement of the difference of height between the concrete surfaces on either compartment of the ‘U’ box. This difference will make clear the self-leveling ability & passing ability of the Self Compacting Concrete (SCC).
- The permissible range for difference h1-h2 is 30mm. a difference of more than 30mm indicates the possibility of blockage with viscosity being on the higher side. If h1-h2 is close to ‘zero’, it shows lower viscosity and concrete could easily pass through.
Fill Box Test
This test is utilized to analyze the filling ability of self-compacting concrete (SCC). The instrument consists of a transparent rectangular box with a number of obstructions through which concrete is made to flow.
The method for conducting this test is discussed below:
- Place the apparatus on firm-level support having a height of 1 meter approximately.
- Fill the concrete mix in the box through the funnel gave at the top of the box until it covers the topmost obstacles at the far end of the box.
- Then measure the height of the concrete at both ends so that the volume of concrete-filled can be calculated.
- Compare the net volume of concrete-filled with respect to the volume of the box up to the top of the topmost obstacles, which gives the filling capacity of SCC.
Acceptance Test Criteria for Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC)
Typical acceptance test criteria for Self Compacting Concrete (SCC) with maximum aggregate size up to 20mm are given in the below table.
| Sr. No | Test | Unit | Acceptable Range of Values |
| 1 | Slump Flow Test | mm | 650-800 |
| 2 | V Funnel T0 V Funnel T5 | Sec. increase over in a sec. | 8-12* 0-3 |
| 3 | L Box (h2/h1) | Ratio | 0.8-1.0 |
| 4 | U Box (h1-h2) | mm | <30 |
| 5 | Fill Box | % | Min 90 (90-100) |
Note:-
- If ‘V’ funnel results are less than 8 sec, decrease the water/powder ratio in the mix. If it is more than 12 sec., increase the water/powder ratio.
- It is the time needed in the slump flow test for concrete to spread by 50 cm.
Typical ranges of values indicate in the above table are based on current knowledge and practice. They have undergone changes with respect to the previous range values. Hence, future developments/experience may lead to further modifications in the ranges indicated. Values outside these ranges may also be acceptable if it can be demonstrated that satisfactory performance is obtained in the specific conditions, e.g. large spaces between reinforcement, layer thickness less than 500mm, the short distance of flow from point of discharge, very few obstructions to pass through in the formwork, very simple design of formwork, etc.






