Abstract
This article describes the precast housing solution developed for rural and semi-urban places in India with the available limited resources and skills. The sole objective was to provide good quality, economical housing solutions to an individual housing builder fulfilling all his needs. This article also addresses the alternative building technologies and materials that affect sustainability features of construction. The sustainable way of construction minimizes the use of water, raw materials, energy, and land and also helps in achieving human health & prosperity.
The goal was to use eco-friendly innovative cement products, use of energy-efficient alternative, and usage of local resources & skills. In order to understand prevailing construction practices, an extensive survey was done at many locations that helped in developing a simple housing solution that requires the least machinery & equipment based on local needs.
In order to demonstrate & experience, one model house of 80 m2 was constructed at plant location by adopting simple precast techniques that can be executed/replicate by semi-skilled manpower by using simple moulds & machines. The first experience was successful resulted in 30% reduce time & 15% saving in construction cost, reduced energy, greenhouse gases, later, the key learning were shared among key stakeholders, who in turn started adopting the techniques fully or partially in their regular constructions.
Introduction
Housing is one of the basic requirements for human survival, owning a house provides significant economic security and dignity in society. As per the 1991 report, there was a housing shortage in the rural was 13.72 million consisting of 3.41 million households without houses and 10.31 million living in unserviceable kutcha houses. It has also been estimated that another 1075 million houses would be needed to cover the population growth in the coming time. The census data further indicates that about 40.82% of the total 112 million rural households remain in one-room quarters, 30.65% in two-room houses, and 13.51% in three-room units or more.
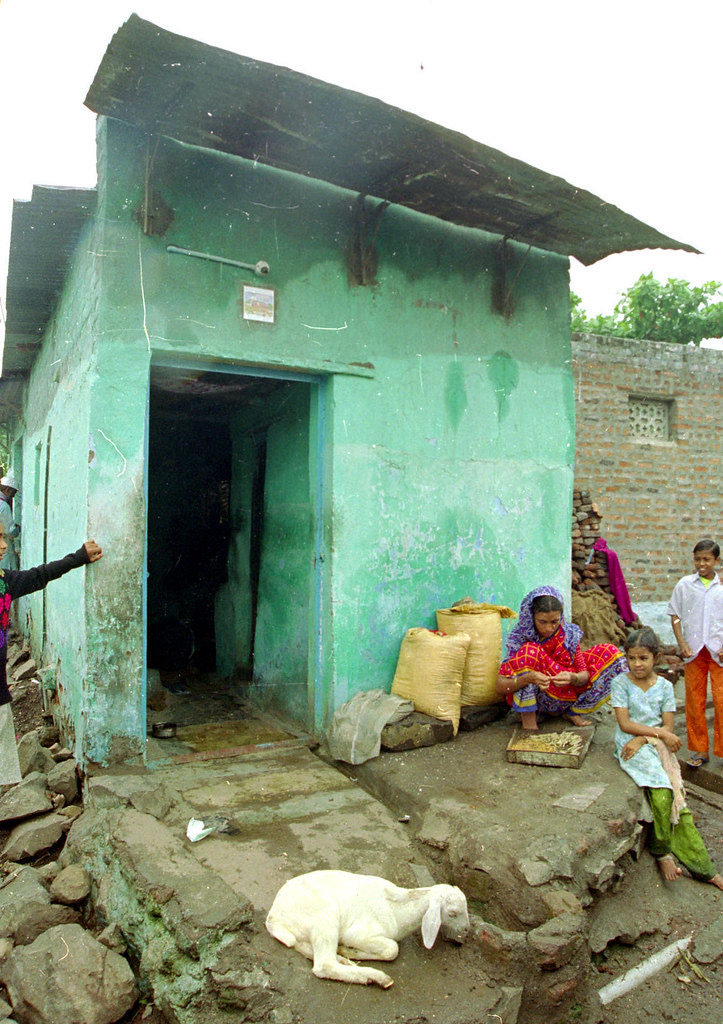



Looking at the present scenario, the survey is done at different locations in the country to understand present construction practices in rural and semi-urban places, noted their requirements. The survey indicated that the requirement of a house ranges from 500 to 1000 Sq.ft with main requirements of one or two-bedrooms with Hall & Kitchen, toilets unit normally preferred separate from the main unit. It was also observed that the houses were not planned by adopting scientific ways which cause costly alternations at later stages; few of the glimpses are in the figure.
Advantages of Precast Housing Technology
The advantages of Precast Housing Technology are manifold:
- Better finish quality, shape, size and aesthetic of precast elements
- Better structural strength through pre-stressing concrete in factory conditions
- Shorter curing times
- Less labor required, less waste generated at the site, and greater scope for automation and minimization of human error
- The self-supporting system eliminates shuttering and scaffolding cost
- More repetitive use of moulds are possible
- Saving time
- Freedom in structural design, full advantage of properties of cement and steel can be exploited
- A similar type of components or sections is produced repeatedly, resulting in increased productivity and economy in cost too
- The construction is not affected due to weather, rain, wind, etc
- The work at the site is diminished to a minimum and therefore, work is qualitatively better, more reliable and clean
The Cost of Precast Housing Technology
The important variables impacting the cost of precast vs. traditional technologies are;
- Material costs (Lower for Precast)
- Labor costs (lower in India than in Northern Europe)
- Initial set-up cap-ex (high for precast)
- Transportation costs (high for precast; depends on distance)
- Lifecycle costs (low for precast; depends on worker skill)
- As labor costs across the board go up in India over time, the better the outlook for precast as the builder will begin to seriously consider it as an alternative.
Sustainable Construction Techniques
Sustainable construction purposes at reducing the environmental impact of building over its entire lifetime, its economic solvency, comfort & safety to its occupants. Sustainable construction can be achieved by selecting materials, methodologies, practices & design philosophy which increase comfort and quality of life while decreasing negative environmental impacts. A building designed and constructed in a sustainable way minimizes the use of water, raw materials, energy, land, and also helps in achieving human health & prosperity. Key sustainable points are,
- Design for minimum waste
- Lean construction & minimize waste
- Minimize energy in construction & use
- Do not pollute
- Preserve & enhance biodiversity
- Conserve water resources
- Respect people & local environment
Project Details
In the first phase, constructed a house 60m2 at plant location comprised of a hall, three-bedroom, lounge, kitchen & toilet.
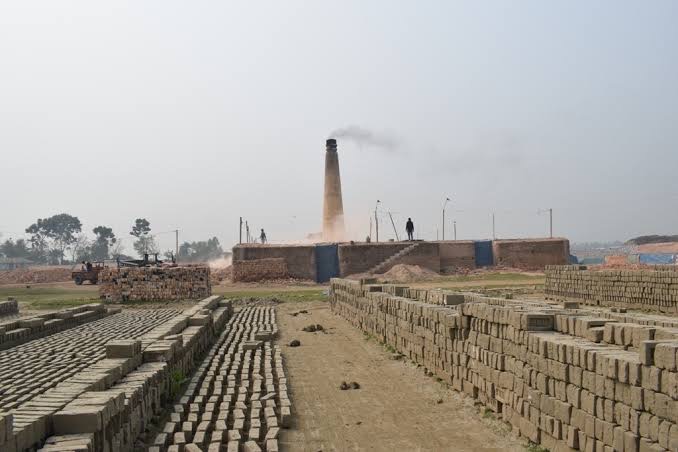
Manufacturing of Precast Elements
In this project, all the RCC components above the plinth level were made up of precast techniques. For casting these components, very simple techniques, moulds, etc were used so that in future one can easily manufacture it without much investment or cost, as shown in the figure.



Masonry Work
Load-bearing masonry 9’’ (Insulated wall technology) was used by placing the bricks on their sides having a cavity of 100 mm with an alternate course of stretchers and headers. The main advantage of this bond is economical in the use of bricks, giving a wall of one brick thickness with fewer bricks than a solid bond. The conventional English bond (9’’ thick wall) required 350 bricks per cu.mt whereas in Rat-trap bond need only 280 bricks also the reduced number of joints reduces the mortar consumption. In summer the temperature inside the house is usually 3o to 5o C lower than the outside ambient temperature and vice versa in winter. The overall saving on the cost of this wall compared to the traditional 9’’ thickness of the wall is about 25%.

Roof – Pre cast RC Plank Roofing System
Precast RC Plank system is used for roofing. This system consists of precast RC planks supported over partially precast joists. The finished slab can be used as an intermediate floor for a living also. The total thickness of the slab is 6 centimeters. RC planks are made with thickness partly varying between 3 centimeters and 6 centimeters. Precast joist is rectangular in shape, 15 centimeters wide and the precast portion is 15 centimeters deep. The above portion is cast while lying in-situ concrete over planks. The stirrups remain projected out of the precast joist. Thus, the total depth of the joist becomes 21 centimeters. an overall economy of 20% is achieved in actual practice compared to the cast-in-situ RCC slab.
Thin Pre-cast Lintel & Sunshade
The use of precast lintels speeds up construction of walls, besides eliminating shuttering and centering. Adoption of thin lintels resulted in a 50% saving in materials and overall cost, compared to conventional lintels.
Composite action of lintel with masonry above is a complex phenomenon which is affected due to bond/friction at the interface of lintel and masonry. The masonry above the lintel acts like an arch & transmits the load to the support of the lintel and the lintel acts like a tie for the arch. For the lintel to act as a tie, it is essential that the bond of friction between the masonry and lintel near support is more than the horizontal shear stress caused by the thrust of the arch.
Verandah MCR Tiles Roofing
For the verandah roof, MCR (Micro concrete roofing tiles) was used consists of 6 mm thick (with thin wire mesh) concrete tiles of size 25 cm x 50 cm. These tiles rest on precast concrete purlins & rafters made by using simple tools & little training.

Stair case
Precast steps of clear width 1 m with tread size – 30 cm. & riser – 18 cm were used. Precast steps directly rest on the 9 masonry wall. This system saves time; shuttering and overall 30% economy was achieved over a conventional system.

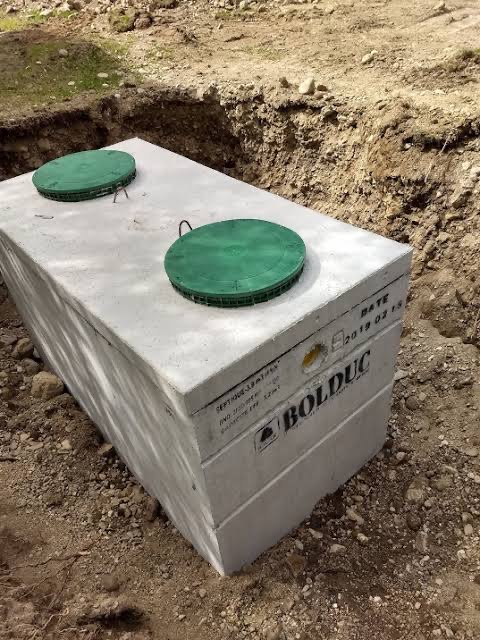
Septic Tank
The circular or rectangular septic tanks constructed with masonry are not 100% watertight and occupy a large area. The effluent quality also deteriorates with time but uses o ferrocement as construction material in septic tanks is advantageous and vertical circular septic tanks can be fabricated, assembled easily. It is 50% cheaper than a conventional tank comprises of precast circular rings.
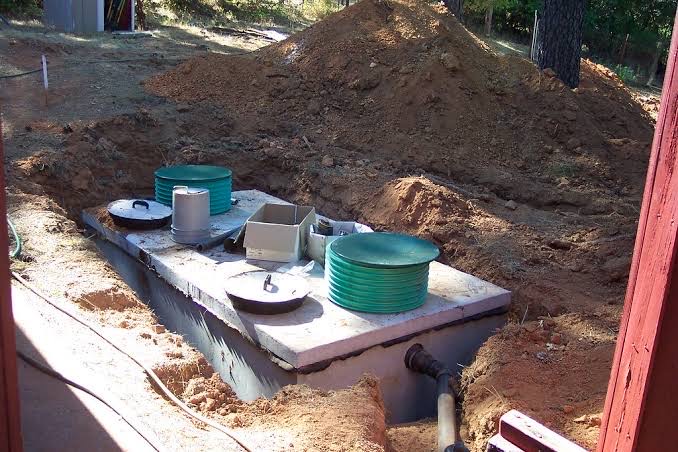


Earthquake Resistance Measures
One of the aspects of sustainable construction is comfort for the occupants, provided concrete band at four levels (Plinth, Sill, Lintel & Roof) as a measure of making it earthquake resistant structure act as a box.
Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting System
Every year an average roof receives about 70,000 liters rainwater, which drains off and ultimately gets wasted. Though India houses nearly 1/5th of the world’s population only 4% of the world’s water resources are found in our country. Water is already on the threshold of crisis in many major cities of India. The application of an appropriate simple rainwater harvesting technology can make possible the utilization of rainwater and it is quite easy to collect rainwater falling on roofs. A simple system as shown in the figure of water collection from the roof was used for recharging the sub-soil. The filtering medium consists of a ferrocement tank filled with a layer of filtering material like coal powder, a graded layer of sand & pebbles. It has a glass window to check for any blockage.

Sustainable Measures Resulted into Saving
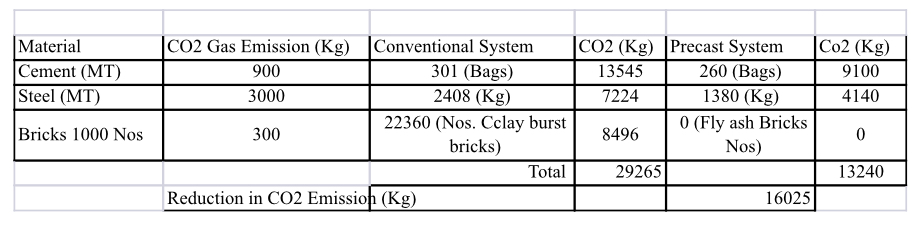
In the entire project, the use of sustainable construction materials, methodology practices & design philosophy resulted in a saving of materials, manpower, energy, and reduced level of greenhouse gases as mentioned in the below table.
| Items | Saving (%) Rs. |
| Cement | 13.62 |
| Steel | 42.69 |
| Bricks | 23.97 |
| Sand | 4.96 |
| Aggregates | 40.47 |
| Formwork | 85.71 |
| Door & Window frames | 58.76 |
| Kitchen Platform | 83.33 |
| Flooring | 45.45 |
| Labour | 52.10 |
| Overall cost | 35.57 |
Indian Realty – Current Scenario in large projects
The face of the realty market in India has changed expediently over the past few years. The large projects comprising of Townships, Mass Housing, IT/ITES parks, and SEZs are of common occurrence these days and will only grow exponentially in the near future.
The majority of many projects are still being constructed using the conventional methods. Thus the instinctive advantage that these projects offer in terms of repetitions and huge volume turnover remains unexploited.
These large scale projects constructed using conventional methods complicate the project management in terms of speed & quality of the construction.
Summery & Conclusion
Precast housing technique proves to be a quality & cost-effective solution for millions of houses required in rural & semi-urban areas. The experience during the construction of all the units clearly indicated that it has the potential of future technology for housing and giving direction to work towards alternative building materials & technologies in order to fulfill huge demand. The quality, speed, energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, cost-effective, employment-generating values associated with these techniques is a boon for the construction industry. We are recommending its use at a mass scale to cop up with the scarcity of natural resources, water, forest, etc is like a wake-up call for all of us in the quest for sustainability.

