Preamble
At many projects, waterlogging at parking & walkways is the major issue especially during monsoon as pavements & floors are normally impermeable. This results in a considerable amount of investment in repairs & providing a stormwater drainage system that may get clog during peak overflow situation. Besides this, there are many other problems that arise due to the above. In such a situation it is very important to think about economical & sustainable which helps in getting all the above problems.
The best solution to above problems is “Pervious Concrete”.
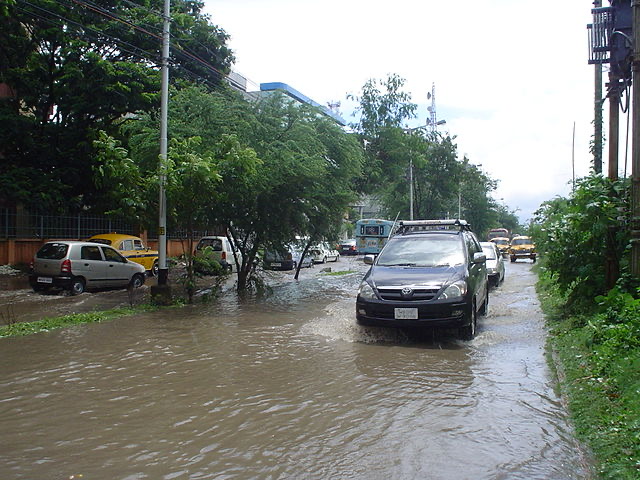


What is Pervious Concrete?
Pervious concrete is a unique, sustainable & economical means to provide complete solutions to important environmental issues and support green construction. By capturing stormwater and allowing it to seep into the ground due to its design properties, pervious concrete is instrumental in recharging groundwater & reducing stormwater runoff. In other words, we term it as “Rain Water Harvesting Concrete”.
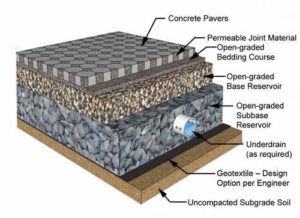
The pervious concrete is a special type of concrete, which consists of cement, coarse aggregates, water and if required, admixtures and other cementitious materials like silica fume, GGBS, fly ash. In Pervious concrete, there are no fine aggregates normally used in the concrete mix design. Hence by the void content is more which allows the water to flow through its body. Therefore, pervious concrete is also known as Permeable Concrete or Porous Concrete.
This concrete technology is helpful in creating more efficient land use by eliminating the need for water retention bodies, costly stormwater drainage & repairing cost which otherwise would have incurred due to water accumulation. In doing so, pervious concrete has the potential to lower overall project costs thus making it more economical.
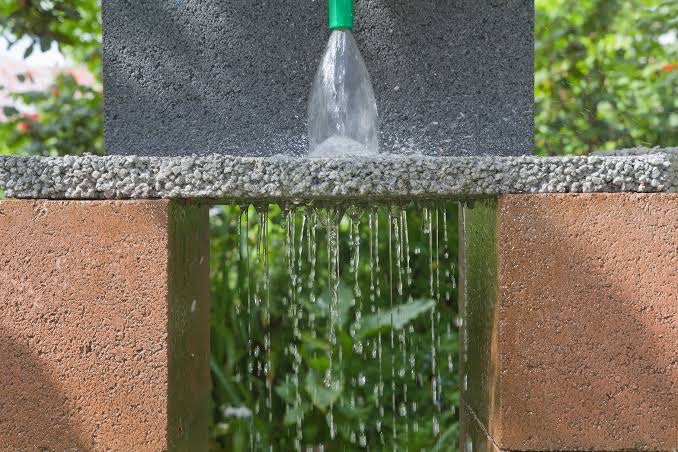

Pervious concrete is typically used in parking areas, areas with light traffic, pedestrian walkways, and greenhouses. It is an important application for sustainable construction.
Why use Pervious concrete?
The proper utilization of Pervious concrete (Permeable concrete) is a recognized Best Management Practice by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency for providing first-flush pollution control and stormwater management. Pervious concrete decreases the runoff from pervious concrete covered areas, which decreases the need for separate stormwater retention ponds and allows the use of smaller capacity storm sewers. This allows property owners or housebuilders to develop a larger area of available property at a lower cost. Pervious concrete also naturally filters stormwater and can reduce pollutant loads entering into streams, ponds, canals, and rivers. Pervious concrete or Permeable Concrete functions like a stormwater retention basin and allows the stormwater to infiltrate the soil over a large area, thus facilitating recharge of groundwater supplies locally. All of these advantages lead to more effective land use.
Pervious concrete or Permeable concrete can also reduce the impact of development on trees. Pervious concrete pavement allows the transfer of both water & air to root systems allowing trees to flourish even in highly developed areas.
How to Design Pervious Concrete?
Pervious concrete is cast from the same materials as conventional concrete, except that there are no or little fine aggregates. The coarse aggregate size of 10mm to 12.5mm and 16mm to 20mm is used to minimize surface roughness and for better aesthetic. However, size can vary from ¼ inch to ½ inch. W/C ratio should be within 0.27 to 0.34. In the manufacturing of pervious concrete Ordinary Portland Cement and Blended Cement can be used. Chemical admixtures like water-reducing admixture or concrete retarder can also be used in pervious concrete.
| Ingredients of Pervious Concrete | |
| Ingredients | Proportions (Kg/m3) |
| Cement | 270 to 415 |
| Aggregate | 1190 to 1480 |
| Water/Cement Ratio | 0.27 to 0.35 |
| Fine to Coarse aggregate ratio | 0 to 1:1 |
| Chemical admixtures or retarders are commonly used. Addition of fine aggregates will decrease the void content but will increase strength. |
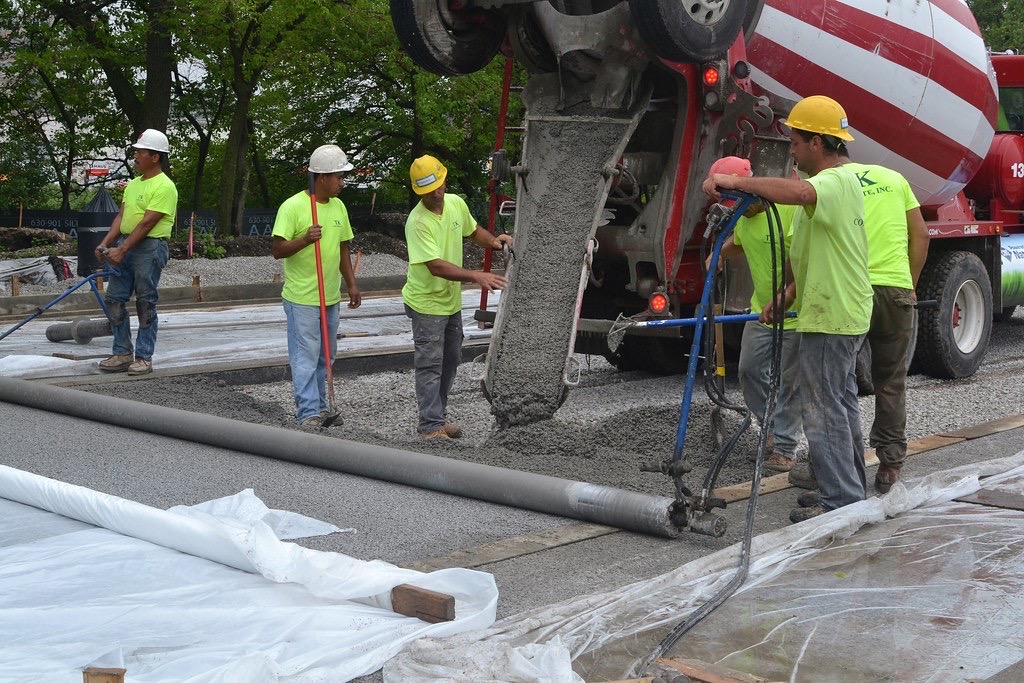
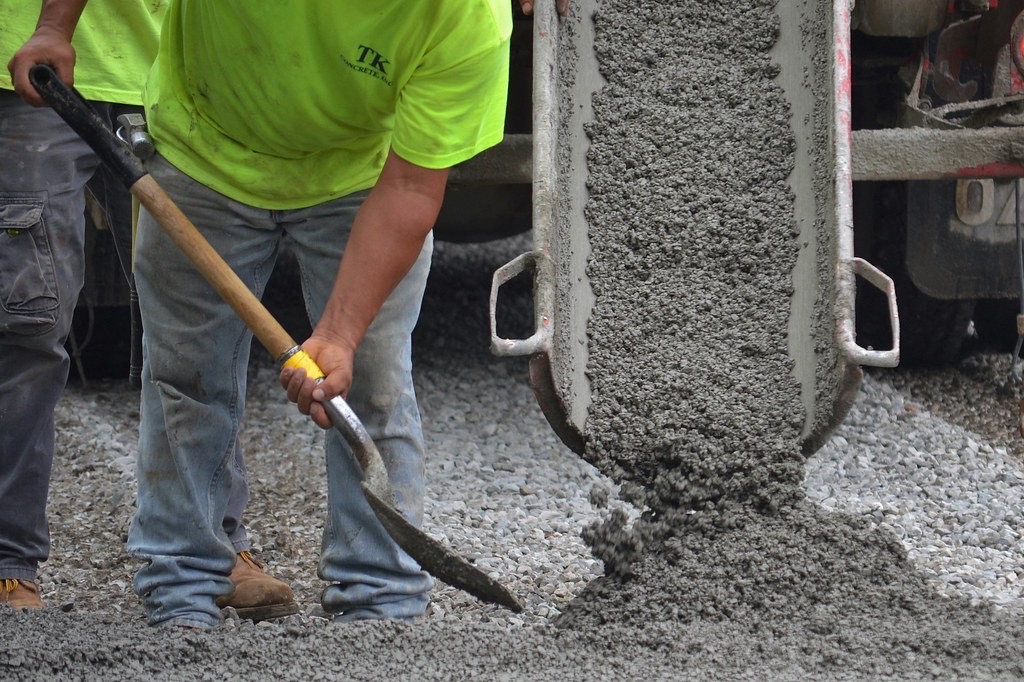


Compressive Test of Pervious Concrete
Compressive strength is dependent on the size of aggregate, void ration, the bond between mortar, and coarse aggregate. In 7 days cubes of pervious concrete gain 30% of its strength, in 21 days of permeable concrete gain 70% of its strength, and for 28 days it gains 95% strength.
Tensile Strength of Pervious Concrete
In Pervious concrete tensile strength vary from 1 Mpa to 3.5 Mpa.
Permeability Test of Pervious Concrete
Permeability of the pervious concrete or permeable concrete is determined by special arrangement of cylindrical shape bucket or specific container which should be open from both the side and has to arrange in such a way so that one side could be used for the pouring of water and other resting on pervious concrete.
Advantages of Pervious Concrete
- Environmental Benefits
- Helps in saving precious water which otherwise goes to drains.
- Helps in keeping earth below wetter, greener & cooler.
- Recharging groundwater level.
- Replace costly water drainage systems.
- Eliminates the use of asphalt which normally causes environmental pollution.
- Use of fly ash thus reducing pollution.
- Protects streams, water shades, and ecosystems.
- Eliminates the need for costly collection and detention systems.
- Development Benefits
- All stormwater piping to detention vaults and ponds & their subsequent maintenance and bonding.
- The need for detention vault or piping systems and their many problematic issues.
- The need for interior plat curbing.
- The oily asphalt road surfaces while replacing them with a thick, rigid concrete surface with a more than 30-year life expectancy.
- Financial Benefits
- A previous infrastructure is much more profit-making for the developer.
- Eliminates time-consuming and costly stormwater detention vaults and piping systems.
- Eliminates the cost of curb and gutter installations.
- Reclaims lots otherwise consumed by vaults and lakes.
- Low maintenance.
- Other Benefits
- Rough texture thus avoiding skidding of vehicles.
- Stronger and durable for light traffic loads.
- Use of local building material
- Economical, lower cost compared to other pavement solutions.
- Conventional construction practices.
- Use of local semi-skilled mason/machinery etc.
Major Application of Pervious Concrete
- Low – volume pavements
- Parking Areas
- Driveways
- Sidewalks
- Roadways
- Overlays
- Swales & Ditches
- Erosion Control
- Slope Protection
- Load-bearing wall
- Residential roads, alleys
- Tennis courts
- Sub-base for conventional concrete pavement
- Hydraulic structures (where permeability is accepted)
- Swimming pool decks
- Pavement edge drains and tree grates in sidewalks
- Groins and seawalls
- Noise Barriers



Caution
In India, we observed that there are chances that the porosity of this pavement may get blocked by the passage of time. Avoid this near sandy area & if it gets blocked same may be cleaned by pressure water jet. It is not recommended for heavy traffic roads.
Conclusion
Pervious Concrete is one of the finest solutions for waterlogging problems, especially at parking & walkways. It also helps in saving precious water. Though the use of such concrete is a very preliminary stage in India but is expected to increase in the future looking to enormous advantages. “Let’s make our earth greener for generations to come.”

